Mutual Funds
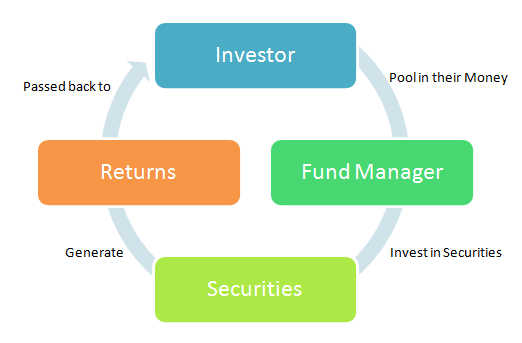
The money pooled in by a large number of people (or investors) is what makes up a Mutual Fund. This fund is managed by a professional fund manager.
It is a trust that collects money from a number of investors who share a common investment objective. Then, it invests the money in equities, bonds, money market instruments and/or other securities. Each investor owns units, which represent a portion of the holdings of the fund. The income/gains generated from this collective investment is distributed proportionately amongst the investors after deducting certain expenses, by calculating a scheme’s “Net Asset Value or NAV. Simply put, a Mutual Fund is one of the most viable investment options for the common man as it offers an opportunity to invest in a diversified, professionally managed basket of securities at a relatively low cost.
Mutual fund explained Graphically
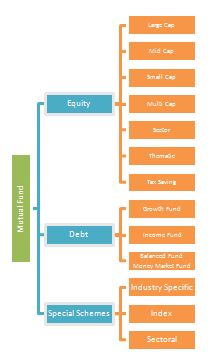
Various types of Mutual Fund schemes exist to cater to different needs of different people. Broadly speaking they can be categorised in 3 segments.
- Equity or Growth Funds
- These invest predominantly in equities i.e. shares of companies
- The primary objective is wealth creation or capital appreciation.
- They have the potential to generate higher return and are best for long term investments.
- Examples would be
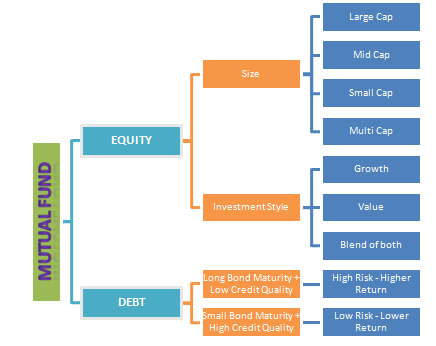
- “Large Cap” funds which invest predominantly in companies that run large established business
- “Mid Cap” funds which invest in mid-sized companies.
- “Small Cap” funds that invest in small sized companies
- “Multi Cap” funds that invest in a mix of large, mid and small sized companies.
- “Sector” funds that invest in companies that are related to one type of business. For e.g. Technology funds that invest only in technology companies
- “Thematic” funds that invest in a common theme. For e.g. Infrastructure funds that invest in companies that will benefit from the growth in the infrastructure segment
- Tax-Saving Funds
- Income or Bond or Fixed Income Funds
- These invest in Fixed Income Securities, like Government Securities or Bonds, Commercial Papers and Debentures, Bank Certificates of Deposits and Money Market instruments like Treasury Bills, Commercial Paper, etc.
- These are relatively safer investments and are suitable for Income Generation.
- Examples would be Liquid, Short Term, Floating Rate, Corporate Debt, Dynamic Bond, Gilt Funds, etc.
- Hybrid Funds
- These invest in both Equities and Fixed Income, thus offering the best of both, as well as .Growth PotentialIncome Generation
- Examples would be Aggressive Balanced Funds, Conservative Balanced Funds, Pension Plans, Child Plans and Monthly Income Plans, etc.
- Other Funds
- Fund of Funds (FoF)
- Exchange Traded Funds (ETF)
- Gold ETF
- International Funds
- Arbitrage Funds
Graphically
Mutual Fund by Category:
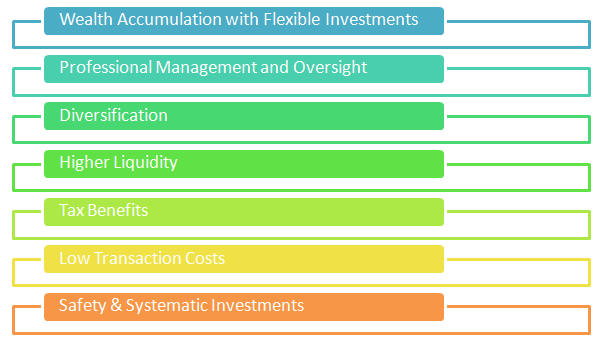
Why should you invest in Mutual Funds?
For more details on mutual funds and investment assistance, seek an appointment or reach out to us on details under contact.
Tekrarlama Saati
fake rolex
replica watches
replika saatler
fake rolex
replica watches